Revenue Cycle Management (RCM) is vital in healthcare. It ensures financial stability and operational efficiency.
RCM involves managing the financial aspects of patient care. This process starts when a patient schedules an appointment.
It ends when the healthcare provider receives full payment. Understanding RCM is crucial for healthcare professionals and administrators.
RCM helps optimize billing processes and improve financial outcomes. It involves several steps, including patient registration and insurance verification.
Accurate coding and timely claim submission are also part of RCM. Effective RCM can enhance cash flow and reduce bad debt.
Technology plays a significant role in streamlining RCM processes. Software solutions automate tasks and reduce errors.
Healthcare facilities can outsource RCM services to specialized companies. This allows providers to focus on patient care.
Understanding the basics of RCM is essential for maintaining financial health in healthcare.
What is Revenue Cycle Management (RCM)?
Revenue Cycle Management (RCM) is a financial process in healthcare. It handles administrative and clinical tasks tied to claims and payments.
RCM starts when patients make appointments, continuing through to full payment collection. It’s essential for identifying, managing, and collecting revenue.
The RCM process includes several key functions. Here are the main components:
- Patient scheduling and registration
- Insurance verification
- Medical coding and charge capture
- Claims submission
- Payment posting and follow-up
Effective RCM is crucial for healthcare providers’ financial health. It improves cash flow, reduces bad debt, and ensures providers are paid timely for services.
In healthcare, RCM stands for ensuring financial stability and operational efficiency. Understanding RCM’s basics can help providers improve billing and collection processes.
Why is Revenue Cycle Management Important in Healthcare?
Revenue Cycle Management is vital in healthcare for several reasons. It guarantees that healthcare providers receive compensation for their services. This financial process supports the sustainability of healthcare organizations.
Timely and accurate reimbursement is critical to maintaining operations. Effective RCM processes help minimize errors and delays in payments. This ensures that healthcare providers have the resources needed for patient care.
RCM also aids in managing expenses and optimizing revenue. Here are some key benefits:
- Enhances cash flow by speeding up the payment process
- Reduces the occurrence of denied claims
- Improves patient satisfaction with clear billing practices
By implementing effective RCM strategies, healthcare organizations can focus more on delivering quality care. It allows clinicians and staff to prioritize patient needs rather than financial concerns. Thus, RCM plays a crucial role in the healthcare system.
Key Terms and RCM Medical Abbreviations Explained
Understanding Revenue Cycle Management (RCM) requires familiarity with specific terms. These terms simplify communication in the medical billing field. Knowing them can enhance efficiency and reduce confusion.
RCM is filled with abbreviations that are used daily. These abbreviations are integral to medical billing and documentation. Learning them is essential for smooth operations.
Here are some key terms and abbreviations you should know:
- RCM: Revenue Cycle Management
- EHR: Electronic Health Records
- CMS: Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services
- EDI: Electronic Data Interchange
- CPT: Current Procedural Terminology
Grasping these concepts helps streamline billing practices. It’s crucial for both new and experienced healthcare staff. By being well-versed, organizations can improve their billing and reimbursement processes.
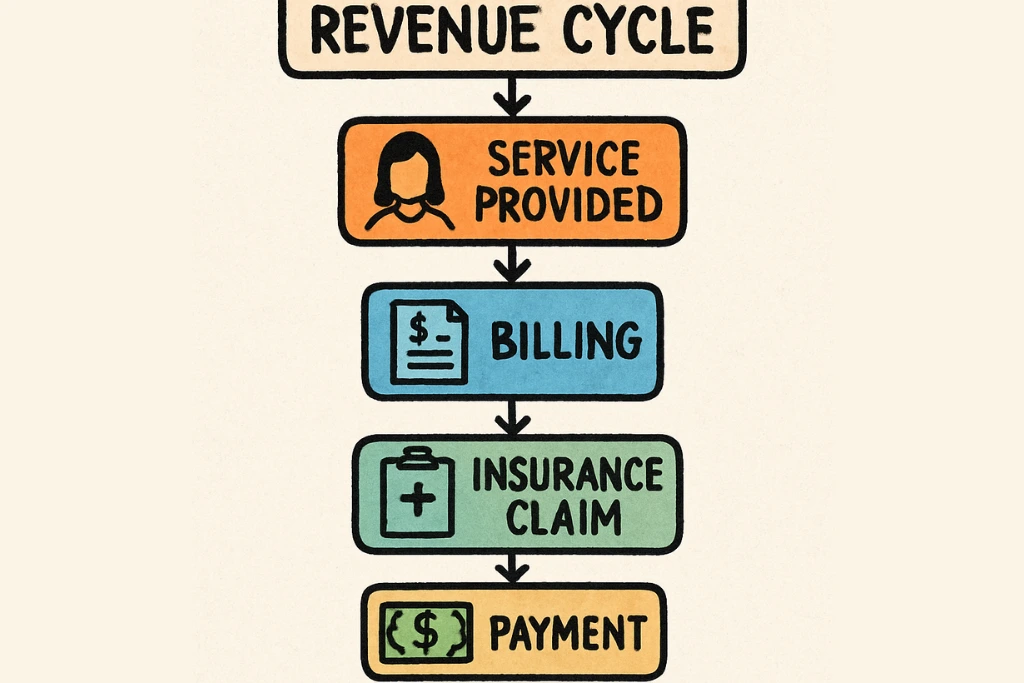
The Revenue Cycle: When Does It Begin and End?
The revenue cycle is a complex process in healthcare. It begins when a patient schedules an appointment. This is the initial step where essential data is gathered.
Throughout the cycle, various steps are completed. These ensure claims are processed and payments collected. The ultimate goal is full financial recompense for services.
The revenue cycle concludes when payments are fully received. This final step marks the end of the process. It confirms that the healthcare provider has been compensated.
Here’s a simple breakdown of the timeline:
- Patient schedules an appointment
- Services rendered to the patient
- Claims processed and payments collected
- Full payment received, cycle ends
Understanding the start and end points is vital. It helps in managing each step effectively. Efficient handling ensures financial stability for healthcare organizations.
Steps in Revenue Cycle Management: The Complete Workflow
Revenue Cycle Management (RCM) involves multiple steps. Each step is crucial in ensuring seamless financial transactions. These steps, if well-coordinated, lead to optimized revenue flow.
The process begins with patient scheduling. This initial step lays the foundation. Patient data collection and insurance details are critical here.
Upon scheduling, the focus shifts to insurance verification. This confirms coverage and pre-authorizes necessary services. Handling this effectively prevents future hiccups.
Charge capture and medical coding follow next. Accurate coding translates medical services into billable charges. Precise coding is essential for successful claims.
Claims submission is the next critical step. Timely processing ensures prompt payment. Any delay here could disrupt cash flow.
Once claims are submitted, payment posting occurs. This ensures the reconciliation of billed and received amounts. Reconciliation confirms that payments match services.
Denials management is crucial for rejected claims. Quick response to denials can recover revenue losses. It involves detailed analysis and appeals.
Patient billing is the final part. Clear communication of dues enhances collection efforts. It involves sending bills and coordinating patient payments.

Patient Scheduling and Registration
The first step is scheduling an appointment. Here, essential patient information is collected. This ensures smooth registration and data accuracy.
Registration is vital for insurance information. Accurate data ensures subsequent processes flow smoothly. Any errors can cause costly delays later.
Insurance Verification and Pre-Authorization
Verification is a crucial step after scheduling. It confirms that the patient has valid insurance. This step prevents surprises in service coverage.
Pre-authorization checks if services need prior approval. It is important for preventing future claim denials. It assures treatment costs align with coverage.
Charge Capture and Medical Coding
Charge capture collects service data for billing. Medical coding translates these services into billable codes. Accurate coding is essential for fair reimbursement.
Key elements in coding include:
- Using standard coding systems like ICD and CPT
- Ensuring coding reflects services rendered
- Checking codes for errors before submission
Claims Submission and Processing
Submitting claims promptly is crucial. Timely submissions ensure faster payments. This step involves transmitting claims to payers.
Processing ensures the claims are reviewed. Any errors can result in delayed payments. Accurate submission reduces processing issues.
Payment Posting and Reconciliation
Payment posting tracks incoming payments. This step includes applying payments to patient accounts. Accurate posting is crucial for correct balances.
Reconciliation ensures payment amounts match billed charges. It prevents discrepancies in financial records. Successful reconciliation confirms accurate account status.
Denials Management and Appeals
Denied claims require swift action. Denials management addresses reasons for denial. Timely appeals increase chances of recovery.
Steps in managing denials include:
- Analyzing denial reasons
- Gathering necessary documentation
- Submitting appeals promptly
Patient Billing and Collections
Final billing informs patients of outstanding dues. Effective billing communication reduces payment delays. It ensures patients understand their financial responsibilities.
Collections focus on retrieving unpaid amounts. Steps in collections include:
- Sending reminders and statements
- Offering payment plans if needed
- Coordinating with collection agencies if required
Engaging patients in the billing process helps. It facilitates timely payments and enhances revenue collection. Clear information exchange is key.
How Does Revenue Cycle Management Work in Practice?
Revenue Cycle Management (RCM) works like an orchestra, where every process plays a vital part. In practice, RCM integrates various administrative and clinical activities. It ensures seamless billing and payment transactions.
Healthcare providers use RCM systems to track patient interactions from start to finish. These systems handle appointments, codes, claims, and payments. This integration ensures that no element is overlooked.
Successful RCM requires attention to detail and constant monitoring. Providers must align their operations with payer requirements and regulatory changes. Key practical elements include:
- Consistent data entry and updates
- Accurate coding and charge capture
- Timely follow-up on unpaid or denied claims
Effective RCM keeps cash flows steady. It helps healthcare providers maintain financial viability. Adapting to changes, it continuously evolves and improves over time.

The Role of Technology in Revenue Cycle Management
Technology plays a crucial role in modern Revenue Cycle Management (RCM). It automates complex processes, reducing manual errors significantly. Leveraging technology ensures efficiency and accuracy in revenue management.
Healthcare providers use various technological tools to streamline RCM. These tools include electronic health records (EHR) and advanced billing systems. Implementing such systems enhances the speed of data processing and claim submissions.
Technology also provides valuable insights through analytics, driving informed decisions. With real-time data access, providers can identify trends and issues quickly. Key technological elements in RCM include:
- EHR systems for patient data management
- Automated billing and coding software
- Analytics tools for financial reporting
Using technology, providers boost financial performance. It supports compliance with regulations, ensuring seamless operations. This tech integration enables faster, more reliable revenue cycles.

Common Challenges in RCM and How to Overcome Them
Revenue Cycle Management (RCM) in healthcare faces several significant challenges. These include errors in medical coding and denied claims. Such issues can severely impact the financial stability of healthcare providers.
To address coding inaccuracies, continuous education and training for coding staff are crucial. Ensuring accurate claim submissions from the start reduces denials. Establishing a dedicated team to manage claims denial is also beneficial. This team can quickly address and rectify rejected claims, reducing overall financial loss.
Moreover, communication breakdowns between clinical and administrative teams can hamper RCM. To prevent this, fostering a culture of collaboration is essential. Regular meetings and seamless information sharing can keep all stakeholders aligned.
Key approaches to overcoming RCM challenges include:
- Investing in staff training and development
- Implementing robust denial management protocols
- Promoting strong interdepartmental communication
Through proactive strategies, providers can enhance revenue cycles and maintain financial health.
Best Practices for Optimizing the RCM Process
Optimizing the Revenue Cycle Management (RCM) process is essential for ensuring financial health in healthcare facilities. Implementing best practices can maximize revenue collection and improve overall efficiency. Start by analyzing the current workflow to identify bottlenecks and areas needing improvement.
Utilize advanced RCM technology to automate routine tasks. Automation reduces manual errors and speeds up the billing process, ultimately boosting revenue. Ensure regular updates and maintenance of software tools to keep processes running smoothly.
Another key practice is fostering patient-centered communication. Educating patients about their financial responsibilities increases transparency. This, in turn, reduces payment delays and improves satisfaction.
Key best practices include:
- Regular process audits and improvements
- Utilizing technology for automation
- Enhancing patient communication and education
By incorporating these strategies, healthcare providers can streamline operations and maintain financial stability.
The Future of Revenue Cycle Management in Healthcare
The future of Revenue Cycle Management (RCM) in healthcare looks promising, with technology playing a pivotal role. As healthcare systems evolve, RCM will likely integrate more advanced technologies like artificial intelligence and machine learning. These innovations promise to enhance the accuracy of claims and speed up processing times.
Moreover, interoperability between systems will be crucial. Ensuring smooth data exchange will help unify billing processes, improving efficiency. Healthcare providers will need to adapt to regulatory changes, requiring continuous learning and flexibility.
Future trends in RCM may include:
- Increased use of AI and machine learning
- Enhanced data interoperability
- Greater regulatory compliance focus
By embracing these developments, healthcare organizations can better manage financial operations and improve patient outcomes.
Conclusion: Key Takeaways for Healthcare Professionals
Understanding Revenue Cycle Management (RCM) is vital for healthcare financial success. A robust RCM process ensures timely payments and reduces financial strain.
Healthcare professionals should focus on enhancing RCM knowledge and adapting to changes effectively. By embracing technology and refining processes, revenue management can significantly improve.
Key takeaways include:
- Continuous learning and adaptation to trends
- Leveraging technology for efficiency
- Prioritizing timely and accurate billing practices
These strategies will support the financial stability of healthcare institutions.






Comments are closed